1. 什么是迭代器?
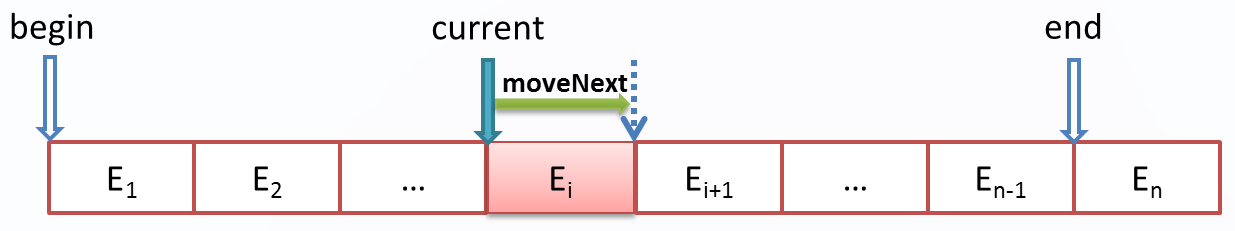
迭代器(Iterator)是按照一定的顺序对一个或多个容器中的元素从前往遍历的一种机制,比如for循环就是一种最简单的迭代器,对一个数组的遍历也是一种的迭代遍历的过程。GOF给出的定义为:提供一种方法访问一个容器(container)对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部细节。迭代器有时也称为枚举器(Enumerator),其结构图如下:
迭代器结构图
迭代器其实就是维护一个当前的指针,这个指针可以指向当前的元素,可以返回当前所指向的元素,可以移到下一个元素的位置,通过这个指针可以遍历容器的所有元素。迭代器一般至少会有以下几种方法:
First(); //将指针移至第一个位置或获得第一个元素
GetCurrent(); //获得当前所指向的元素
MoveNext(); //移至下一个元素
2. 如何使用迭代器
既然迭代器是封装里面的实现细节,对外提供方便访问容器元素的接口,那我们就先从使用的角度认识迭代器,看看C++是如何使用迭代器的。
迭代器示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| void TestIterator()
{
vector<int> vec;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i*2);
}
cout << "iterator vector:" << endl;
for(vector<int>::iterator itr = vec.begin(); itr != vec.end(); itr ++)
{
cout << *itr << " ";
}
cout << endl;
map<int, string> student;
student.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "张三"));
student.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "王五"));
student.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "李四"));
cout << "iterator map:" << endl;
for (map<int, string>::iterator itr = student.begin(); itr != student.end(); itr ++)
{
cout << itr->first << "-->" << itr->second << endl;
}
}
|
结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| iterator vector:
0 2 4 6 8
iterator map:
1-->张三
2-->李四
3-->王五
|
3. C++迭代器说明
c++中的容器(如vector、map、list、set等)一般会提供四个迭代器:
- iterator:正向迭代,从前往后遍历,可修改元素的值
- const_iterator:正向常量迭代,但不能修改元素的值,因为指向的是const的引用
- reverse_iterator:反向迭代,从后往前遍历,可修改元素的值
- const_reverse_iterator:反向常量迭代,但不能修改元素的值,因为指向的是const的引用
每一种迭代器都提供一对首尾位置的标志begin和end,其关系如下:
| 迭代器类型 |
开始位置标志 |
末尾位置标志 |
说明 |
| iterator |
begin() |
end() |
正向迭代 |
| const_iterator |
cbegin() |
cend() |
正向常量迭代 |
| reverse_iterator |
rbegin() |
rend() |
反向迭代 |
| const_reverse_iterator |
crbegin() |
crend() |
反向常量迭代 |
对应的示意图如下:
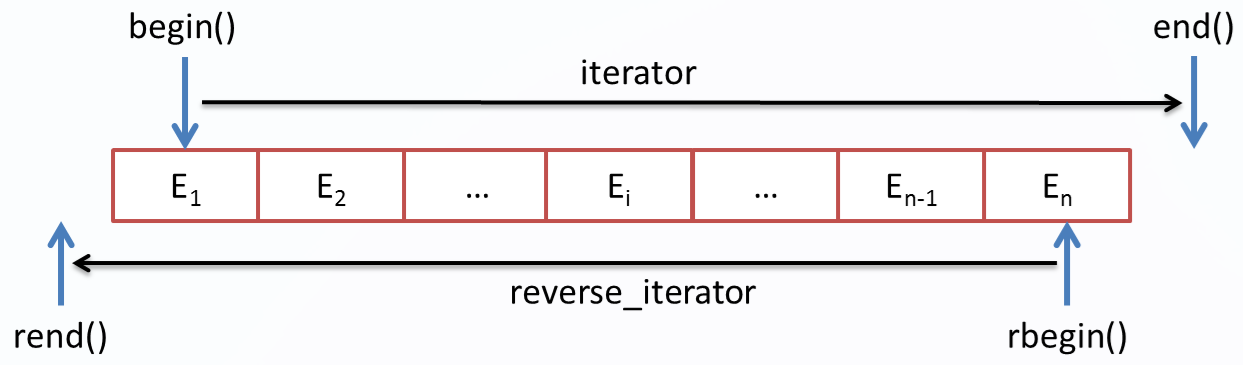
图1:正常的迭代
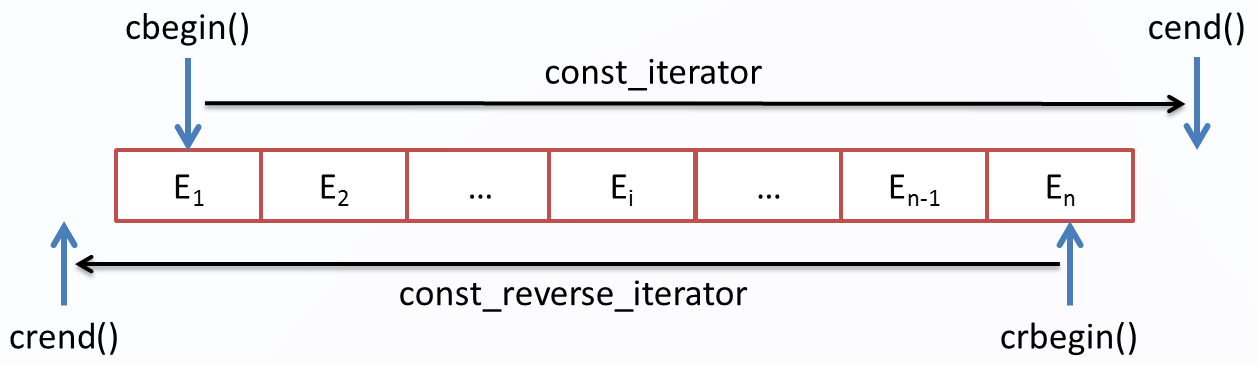
图2:常量值的迭代
4. 迭代器的高级应用
以上讲述的迭代器基本都是集合内部的元素具有相同的数据类型,但实际的开发过程中可能会有更复杂的容器结构,假设有如下的需要:
一个公司有多个部门,每个部门有多个人组成,这些人中有开发人员,有测试人员,和与项目相关的其它人员,其结构如下:
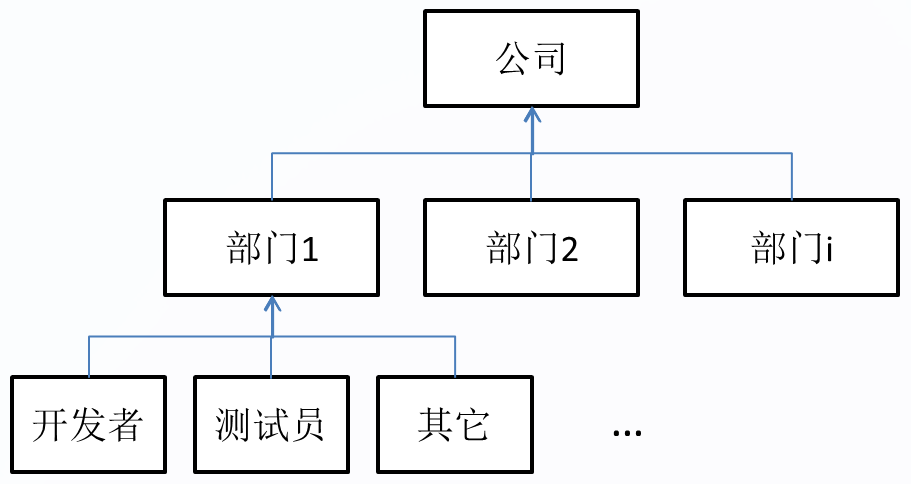
现在要遍历这个公司的所有开发人员,遍历这个公司的所有测试人员。
针对这个需求,我们可以创建一个定制化的迭代器来遍历一个公司所有人员,也可以传入员工类型来遍历指定类型的员工,其类的结构图如下:
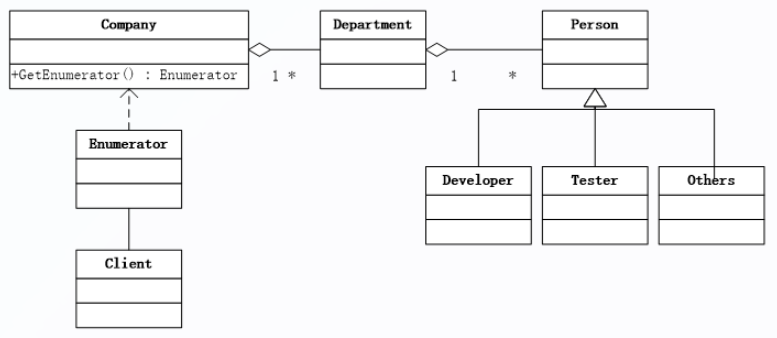
对应的代码实现如下。
4.1. Enumerator.hpp
迭代器类Enumerator的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| #pragma once
#include <string>
#include "Company.h"
class Enumerator
{
public:
Enumerator(const Company& company, PersonType type)
: company_(company)
, person_type_(type)
{
}
~Enumerator() = default;
public:
void Reset()
{
cur_department_index_ = 0;
cur_person_index_ = 0;
}
const Person* Current()
{
if (cur_department_index_ >= 0 && cur_department_index_ < company_.GetDepartmentSize() &&
cur_person_index_ >= 0 &&
cur_person_index_ < company_.GetDepartment(cur_department_index_)->GetPersonSize())
{
return company_.GetDepartment(cur_department_index_)->GetPerson(cur_person_index_);
}
return nullptr;
}
bool MoveNext()
{
cur_person_index_++;
bool isLoop = true;
for (int i = cur_department_index_; i < company_.GetDepartmentSize() && isLoop; ++i)
{
for (int j = cur_person_index_;
j < company_.GetDepartment(i)->GetPersonSize() && isLoop;
++j)
{
const Person* person = company_.GetDepartment(i)->GetPerson(j);
if (person->GetType() == person_type_ || person_type_ == PersonType::All)
{
isLoop = false;
}
if (isLoop)
{
cur_person_index_++;
}
}
if (isLoop)
{
cur_department_index_++;
cur_person_index_ = 0;
}
}
auto result =
cur_department_index_ >= 0 && cur_department_index_ < company_.GetDepartmentSize() &&
cur_person_index_ >= 0 &&
cur_person_index_ < company_.GetDepartment(cur_department_index_)->GetPersonSize();
return result;
}
private:
PersonType person_type_;
const Company& company_{ nullptr };
int cur_department_index_{ 0 };
int cur_person_index_{ -1 };
};
|
4.2. Iterator.cpp
调用代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| #include "Company.h"
#include "Enumerator.hpp"
#include "Person.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
int main()
{
int empId = 1;
auto pPerson11 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer11", "C++", "智慧城市");
auto pPerson12 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer12", "Java", "智慧城市");
auto pPerson13 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer13", "JavaScript", "智慧城市");
auto pPerson14 = new Tester(empId++, "Tester15", "LoadRunner");
auto pPerson15 = new Tester(empId++, "Tester16", "黑盒测试");
auto pDepartMent1 = new Department("开发1部");
pDepartMent1->AddPerson(pPerson11);
pDepartMent1->AddPerson(pPerson12);
pDepartMent1->AddPerson(pPerson13);
pDepartMent1->AddPerson(pPerson14);
pDepartMent1->AddPerson(pPerson15);
auto pPerson21 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer21", "IOS", "智能语音");
auto pPerson22 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer22", "Android", "智能语音");
auto pPerson23 = new Tester(empId++, "Tester24", "TestIn");
auto pDepartMent2 = new Department("开发2部");
pDepartMent2->AddPerson(pPerson21);
pDepartMent2->AddPerson(pPerson22);
pDepartMent2->AddPerson(pPerson23);
auto pPerson31 = new Developer(empId++, "Developer31", "C++", "电子书内核");
auto pPerson32 = new Tester(empId++, "Tester35", "LoadRunner");
auto pDepartMent3 = new Department("内核研发部");
pDepartMent3->AddPerson(pPerson31);
pDepartMent3->AddPerson(pPerson32);
Company company("阳光教育");
company.AddDepartment(pDepartMent1);
company.AddDepartment(pDepartMent2);
company.AddDepartment(pDepartMent3);
std::cout << "遍历所有开发者:" << std::endl;
Enumerator enumerator1 = company.GetEnumerator(PersonType::Developer);
while (enumerator1.MoveNext())
{
const Person* pPerson = enumerator1.Current();
if (pPerson)
{
pPerson->showInfo();
}
}
std::cout << "遍历所有测试人员:" << std::endl;
Enumerator enumerator2 = company.GetEnumerator(PersonType::Tester);
while (enumerator2.MoveNext())
{
const Person* pPerson = enumerator2.Current();
if (pPerson)
{
pPerson->showInfo();
}
}
std::cout << "遍历公司所有员工:" << std::endl;
Enumerator enumerator3 = company.GetEnumerator(PersonType::All);
while (enumerator3.MoveNext())
{
const Person* pPerson = enumerator3.Current();
if (pPerson)
{
pPerson->showInfo();
}
}
return 0;
}
|
4.3. 输出结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| 遍历所有开发者:
员工:1-Developer11 开发工程师,擅长语言:C++,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:2-Developer12 开发工程师,擅长语言:Java,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:3-Developer13 开发工程师,擅长语言:JavaScript,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:6-Developer21 开发工程师,擅长语言:IOS,负责项目:智能语音
员工:7-Developer22 开发工程师,擅长语言:Android,负责项目:智能语音
员工:9-Developer31 开发工程师,擅长语言:C++,负责项目:电子书内核
遍历所有测试人员:
员工:4-Tester15 测试工程师,测试类型:LoadRunner
员工:5-Tester16 测试工程师,测试类型:黑盒测试
员工:8-Tester24 测试工程师,测试类型:TestIn
员工:10-Tester35 测试工程师,测试类型:LoadRunner
遍历公司所有员工:
员工:1-Developer11 开发工程师,擅长语言:C++,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:2-Developer12 开发工程师,擅长语言:Java,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:3-Developer13 开发工程师,擅长语言:JavaScript,负责项目:智慧城市
员工:4-Tester15 测试工程师,测试类型:LoadRunner
员工:5-Tester16 测试工程师,测试类型:黑盒测试
员工:6-Developer21 开发工程师,擅长语言:IOS,负责项目:智能语音
员工:7-Developer22 开发工程师,擅长语言:Android,负责项目:智能语音
员工:8-Tester24 测试工程师,测试类型:TestIn
员工:9-Developer31 开发工程师,擅长语言:C++,负责项目:电子书内核
员工:10-Tester35 测试工程师,测试类型:LoadRunner
|
4.4. 更多详细代码
https://gitee.com/spencer_luo/iterator
这样就使得代码简洁易懂易读。
迭代器的应用场景:
- 集合的内部结构复杂,不想暴露对象的内部细节,只提供精简的访问方式。
- 需要提供统一的访问接口,从而对不同的集合使用同一的算法。









